The Dangers and Risks of Self-Medication with Antibiotics and Alternative Approaches
Uncategorized Pharmacy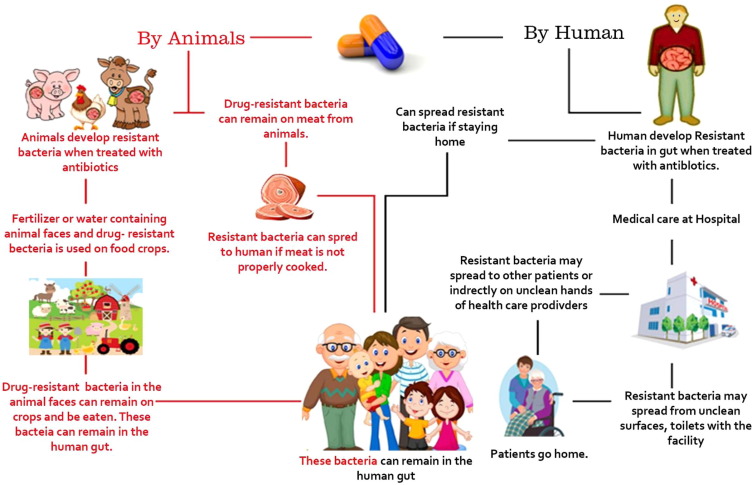
Introduction:
Self-medication has become increasingly common in today’s society, where individuals are inclined to seek quick remedies for their health issues. Antibiotics, in particular, are frequently misused and overused by people without proper medical supervision. This article aims to shed light on the dangers and risks associated with self-medication of antibiotics, emphasizing the importance of responsible use and consulting healthcare professionals
1. The Problem of Self-Medication:
Self-medication refers to the practice of treating one’s own ailments without consulting a healthcare professional. While self-medication can be appropriate for minor conditions, it becomes concerning when it involves the usage of potent drugs like antibiotics. People often resort to this approach due to convenience, lack of awareness, or the desire to avoid medical expenses.
2. Understanding Antibiotics:
Antibiotics are powerful drugs designed to combat bacterial infections. They work by targeting and killing bacteria or inhibiting their growth. However, antibiotics are ineffective against viral infections such as the common cold or flu. Misusing antibiotics can lead to adverse effects, antibiotic resistance, and hamper their efficacy when genuinely needed.
3. Risk Factors of Self-Medication with Antibiotics:
a) Inaccurate Diagnosis: Self-medication runs the risk of misdiagnosing the underlying condition. Without proper medical examination, it is challenging to differentiate between bacterial and viral infections, leading to the unnecessary use of antibiotics.
b) Adverse Effects: Antibiotics can cause various side effects, ranging from mild symptoms like nausea or diarrhea to severe allergic reactions. Without proper medical guidance, individuals may not recognize these adverse effects, leading to further complications.
c) Antibiotic Resistance: Overuse and misuse of antibiotics contribute significantly to the emergence and spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. When antibiotics are taken unnecessarily or improperly, bacteria can develop resistance, rendering the drugs ineffective in treating serious infections.
d) Delayed Proper Treatment: By opting for self-medication, individuals may delay receiving the necessary medical attention. Delaying proper treatment can worsen the condition, allowing the infection to progress and potentially lead to severe complications.
4.Promoting Responsible Antibiotic Use:
a) Awareness and Education: Public awareness campaigns highlighting the risks associated with self-medication and promoting responsible use of antibiotics are crucial. Educating individuals about the appropriate indications, dosage, and duration of antibiotic treatment can help them make informed decisions.
b) Prescription-Only Antibiotics: Regulatory measures restricting the availability of antibiotics without a prescription can discourage self-medication. Pharmacists and healthcare professionals play a vital role in ensuring that antibiotics are dispensed appropriately.
c) Seeking Professional Medical Advice: Consulting a healthcare professional before starting any antibiotic treatment is crucial. They can accurately diagnose the condition, prescribe the correct antibiotic, and provide guidance on its proper use.
d) Antibiotic Stewardship Programs: Healthcare institutions should implement antibiotic stewardship programs to monitor and optimize antibiotic usage. These programs help track antibiotic prescriptions, educate healthcare professionals, and encourage the appropriate use of antibiotics.
a) Prevention and Lifestyle Changes: Emphasize the importance of preventive measures such as proper hygiene, vaccinations, and a healthy lifestyle. These practices can reduce the risk of infections and minimize the need for antibiotics.
b) Natural Remedies: Encourage individuals to explore natural remedies for minor ailments. While these remedies may not replace antibiotics for serious infections, they can provide relief for mild symptoms and support the body’s defense mechanisms.
c) Communication with Healthcare Providers: Open communication with healthcare professionals is vital. Individuals should inform their doctors about any ongoing self-medication or previous antibiotic use to ensure proper assessment and treatment.
d) Responsible Disposal of Unused Antibiotics: It is crucial to dispose of any leftover antibiotics responsibly. Unused antibiotics should not be saved for future use or shared with others, as this can contribute to antibiotic resistance. Follow local guidelines for proper disposal methods.
6. The Role of Technology:
Advancements in technology have made healthcare more accessible. Telemedicine platforms and health apps can provide a convenient and reliable means to consult healthcare professionals remotely, reducing the likelihood of self-medication without appropriate guidance. These resources can also provide valuable information, generate awareness, and promote responsible antibiotic use.
The Pros and Cons of Self-Medicating: A Pragmatic Approach
Self-medication, the act of treating minor illnesses or symptoms without consulting a healthcare professional, has become increasingly common among individuals seeking quick relief or cost-effective solutions. While self-medication can sometimes provide effective short-term relief, it is important to consider the potential risks and limitations associated with this practice. In this blog post, we will explore the pros and cons of self-medication and offer pragmatic advice for those considering self-treatment.
Pros of Self-Medication:
1. Convenience and Accessibility:
One of the primary advantages of self-medication is the convenience it provides. Over-the-counter medications, such as pain relievers or antihistamines, can often be easily purchased from pharmacies or supermarkets without a prescription. This accessibility allows individuals to address minor ailments promptly, without the need for a doctor’s appointment.
2. Cost-Efficiency:
Another appealing aspect of self-medication is the potential cost savings. By avoiding consultations and prescriptions, individuals can save money on healthcare expenses. Generic versions of many medications are often available at a lower cost, making self-medication an attractive option for those on a tight budget.
3. Non-Critical Conditions:
Self-medication is generally suitable for managing common non-critical conditions, such as colds, headaches, or mild allergies, which often have well-established treatments and over-the-counter options available. For such conditions, self-treatment can prove effective and allow individuals to regain their well-being without the need for professional intervention.
Cons of Self-Medication:
1. Misdiagnosis:
One of the most significant risks associated with self-medication is the potential for misdiagnosis. Without proper medical training, individuals may misunderstand symptoms, leading to inaccurate self-diagnosis. This can result in the use of inappropriate medications or treatments, potentially exacerbating the condition or delaying proper medical attention.
2. Masking Underlying Issues:
Following from the previous point, self-medication can merely mask the symptoms of an underlying medical condition. While treating the symptoms may provide temporary relief, it is crucial to address the root cause of the problem. A healthcare professional’s involvement is vital for identifying and treating the underlying issue effectively.
3. Adverse Reactions and Interactions:
While over-the-counter medications may seem harmless, they can still have adverse reactions or interact with existing medications. Some individuals may have allergies or sensitivities to certain substances, making self-medication risky without proper knowledge of potential drug interactions or contraindications. Consulting a healthcare professional can help ensure safe usage and minimize any potential risks.
Pragmatic Approaches to Self-Medication:
1. Educate Yourself:
Before attempting to self-medicate, take the time to educate yourself on the condition, symptoms, and possible treatments. Reliable sources such as reputable websites, medical literature, or trusted healthcare professionals can provide valuable information to aid your decision-making process.
2. Follow Package Instructions:
If you opt for over-the-counter medications, carefully read and follow the instructions provided on the packaging. Ensure you understand the recommended dosage, potential side effects, and any precautions or warnings associated with the medication.
3. Know When to Seek Professional Help:
Recognize the limitations of self-medication and understand when it is necessary to consult a healthcare professional. If symptoms persist, worsen, or if you are uncertain about the diagnosis or treatment, it is advisable to seek professional assistance promptly.
Self-medication can offer convenience and cost savings for minor ailments, but it is crucial to understand its limitations and potential risks. Educating your
of responsible self-medication. While self-treatment can be an effective and affordable option for minor ailments, it is important to exercise caution and make informed decisions to ensure optimal health outcomes.
4. Avoiding Self-Diagnosis:
As mentioned earlier, self-diagnosis can be a significant pitfall of self-medication. Instead of relying solely on personal assessments, it is advisable to seek professional advice when experiencing unfamiliar or persistent symptoms. Healthcare professionals possess the necessary knowledge and expertise to accurately diagnose and treat various medical conditions.
5. Temporary Solution:
Self-medication should only be considered a temporary solution for short-term relief of common symptoms. If the symptoms persist or worsen over time, it is crucial to seek appropriate medical attention. Certain conditions may require specific treatment plans or interventions beyond the scope of self-medication.
6. Prevention is Key:
In addition to self-medication, adopting preventive measures is essential for maintaining good health. Engaging in a healthy lifestyle, maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and practicing good hygiene can minimize the occurrence of common ailments. By focusing on overall wellness, you may reduce the need for self-medication in the long run.
7. Herbal Remedies and Supplements:
When considering self-medication, some individuals turn to herbal remedies or dietary supplements. While certain herbs and supplements may offer potential health benefits, it is essential to exercise caution. These alternative treatments can still have side effects or interact with other medications. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or a qualified herbalist before integrating them into your self-medication regimen.
8. Responsible Use of Over-the-Counter Medications:
When using over-the-counter medications, it is vital to adhere to recommended dosages and usage guidelines. Avoid exceeding the recommended dose, as it can lead to adverse reactions or toxicity. If you are unsure about a particular medication or its suitability for your condition, consult with a pharmacist or healthcare professional for guidance.
Remember, self-medication should never substitute for professional medical care when necessary. Healthcare professionals possess the expertise to make accurate diagnoses, prescribe appropriate treatments, and provide necessary guidance. Self-medication is most effective and safe when used cautiously and responsibly, in conjunction with professional medical advice when needed.
Self-medication refers to the practice of individuals diagnosing and treating their own health conditions without seeking professional medical help. This practice is common in both rural and urban areas, although there may be differences in the types of ailments treated and the availability of healthcare resources.
In rural areas, access to healthcare facilities and professionals may be limited. People may have to travel long distances to reach a doctor or a pharmacy, and they may face challenges such as transportation issues or financial constraints. As a result, individuals in rural areas often resort to self-medication as a means to address minor illnesses or manage chronic conditions.
Commonly self-medicated ailments in rural areas include headaches, fever, common cold, cough, minor wounds, and digestive issues. Local herbal remedies, traditional remedies, or over-the-counter drugs are commonly used for self-treatment. However, it is essential to note that self-medication in rural areas can also carry risks, as individuals may lack proper knowledge about appropriate dosages, contraindications, and potential side effects.In urban areas, healthcare facilities are more readily available, and people may have easier access to doctors, clinics, and pharmacies. However, urban areas also face their own challenges. Due to long working hours, busy lifestyles, and limited time, individuals may opt for self-medication to address minor health problems quickly without the need for a doctor’s appointment.Self-medication in urban areas often involves medications for common ailments like headaches, allergies, mild digestive problems, minor infections, or sleep issues. Over-the-counter medications, such as pain relievers, antihistamines, and topical creams, are frequently used for self-treatment. Urban areas may also have a broader range of options available, including a variety of pharmaceutical products and the convenience of online shopping. While self-medication can provide immediate relief for minor health issues, it’s important to exercise caution. Self-medication should only be considered for mild and well-understood conditions. Serious or chronic illnesses, unclear symptoms, or persistent problems should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional to ensure accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
In both rural and urban areas, promoting health literacy and raising awareness about the potential risks of self-medication is crucial. Encouraging individuals to seek professional healthcare advice when necessary and providing proper education on the appropriate use of medications can help promote safe and responsible self-care practices.
Conclusion:
The rise in self-medication practices, especially with antibiotics, poses serious risks to public health. The improper use of antibiotics contributes to adverse effects, antibiotic resistance, and delays in receiving proper treatment. Responsible antibiotic use, including seeking professional medical advice and adhering to prescribed guidelines, is essential for effective treatment and reducing the emergence of antibiotic resistance. Self-medication of antibiotics poses numerous risks and dangers for individuals and public health. The improper use of antibiotics leads to adverse effects, antibiotic resistance, and delayed proper treatment. It is essential to raise awareness about the consequences of self-medication and promote responsible antibiotic use through education, regulation, and proactive measures. By consulting healthcare professionals, understanding antibiotic indications, and adopting preventive measures, individuals can play a crucial role in minimizing the misuse of antibiotics and preserving their effectiveness for future generations. Ultimately, a collaborative effort between healthcare providers, regulatory bodies, and the public is necessary to address this pressing issue and ensure the responsible use of antibiotics.

Mr. Ajay
Geeta University (Panipat)
Related Posts
The Imperative of Efficiently Managing Wealth: Building Financial Resilience in a Dynamic World
Introduction In an era marked by economic volatility and uncertainty, the significance of managing one’s wealth efficiently cannot be overstated. Wealth management encompasses a spectrum of strategies and practices aimed at optimizing financial resources, securing future goals, and navigating the

Exploring Explosives and its analysis with Forensic Science
Introduction Explosives, with their immense power and destructive potential, have captivated the human imagination for centuries. From military applications to industrial uses and criminal activities, explosives play a significant role in various aspects of modern society. However, understanding the nature
The Power of Positive Attitude: A Soft Skill Trainer’s Perspective on Success
Introduction In the dynamic landscape of personal and professional development, the significance of soft skills cannot be overstated. Among these, one of the most influential factors is the attitude individuals bring to their endeavors. As a seasoned soft skills trainer,

