The Male Hormone Journey: Navigating Andropause
Uncategorized Pharmacy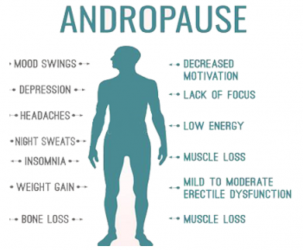
What is Andropause?
The term “andropause” is often used interchangeably with the term “menopause,” which refers to the hormonal changes that occur as men age. However, doctors are still divided as to whether men really go through a “man version” of andropause, or if andropause itself is a type of hypocrinosis that affects a significant portion of the aged men’s population. Unlike women, men’s sex hormones don’t “stop working” as they age. Instead, they undergo a gradual decline. Healthy men experience this decline so slowly that it may not affect them until they are in their 80s or older. Low testosterone levels in predisposed men may affect reproduction as early as 45-50 years of age, with symptoms becoming fully apparent at a later age (70+ on average).
Low testosterone levels are the primary cause of “andropause.” Testosterone supposedly declines roughly 1% every year from the time a man is somewhere in the range of 30 and 40 years of age, being generally 65% the levels found in youth on normal when a man arrives at his 70s.
Testosterone is made by Leydig cells in the testicles. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland, which release gonadotropin-releasing hormone and gonadotropins like luteinizing hormone, respectively, instruct the testes to produce testosterone. Luteinizing chemical animates an expansion in testosterone creation and is set free from the mind in a progression of heartbeats at various seasons of the circadian cycle.
Its creation is a for all intents and purposes stable interaction that can hypothetically last a man as long as he can remember and longer. Current living and age-related factors anyway can find a man and diminishing testosterone creation. These incorporate expanded recurrence of contracting diseases, dietary inadequacies, uplifted profound pressure and diminished active work.
Certain metabolic infections, for example, diabetes and weight can build the gamble for hypogonadism and a level of young fellows with these circumstances as of now experience the ill effects of low testosterone levels. Harm to the testicles can likewise bring about lower testosterone creation, as can a higher admission of poisons like cadmium.
Fascinating examinations feature that in populaces of ancestral men, andropause is far more extraordinary than in the West and testosterone levels of ancestral men stay more consistent than found in Western partners
Side effects of andropause are equivalent to hypogonadism, testosterone inadequacy and the late phases of male ageing. They include:
Prostatic amplification
Loss of charisma
Decreased sexual capability
Lower energy levels
Muscle shortcoming
Sadness
Decreased insusceptible capability
A few men likewise get hot flushes like ladies with menopause. Rest aggravations, mind-set swings (particularly crabbiness) and stomach weight gain are different side effects related to male ageing. Erectile dysfunction and urination issues can eventually arise from testosterone deficiency.
The complete end of testosterone creation doesn’t happen in male menopause, however happens in the instances of prostatic malignant growth and either compound or actual maiming.
DIAGNOSING ANDROPAUSE
Andropause is certainly not an authority condition that can be analysed, but low testosterone levels and hypogonadism can be analysed. As can a condition that is related, like harmless prostatic hyperplasia. Because the majority of men ignore symptoms associated with moderate testosterone decline, it is typically only possible to make a diagnosis of hypogonadism when symptoms begin to affect one’s quality of life.
A specialist will initially take a case history and on the off chance that side effects add up, they will first probably look at the prostate to ensure not prostate extension is causing the issue. After an actual assessment, blood tests might be requested to test chemical levels as well as markers for other regenerative irregularities. Without even a trace of sickness, testosterone decline or inadequacy can then be analysed. Out-and-out lack will in general influence under 20% of men in their 70s and, surprisingly, less in more youthful ageing men.
As testosterone levels vacillate over the day, it ought to be noticed that blood tests might be rehashed to work on the exactness of the outcomes.
HARMLESS PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA:
: A Typical Topic in Male Maturing
Harmless prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is an undeniably more probable determination for an old man with steady urinary and regenerative side effects. This condition happens in up to 90% of all matured men carrying on with a cutting-edge way of life after arriving in their 80s or 90s and is brought about by disturbances in prostatic androgen signalling.
The illness is a result of high prostatic testosterone, especially its more powerful structure, dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT has a strength of up to multiple times that of typical testosterone and makes the organ develop a lot bigger.
Ultimately, the organ can to some extent block the urinary parcel, causing disturbance, torment and different issues while passing pee. Over the long haul, the bladder and sensory system likewise become influenced, causing bladder impediments, misleading impressions of urinary earnestness and rest disturbances.
The degrees of testosterone in the circulation system aren’t guaranteed to mirror the levels in the prostate. Even though chemicals decline with maturing, prostatic testosterone levels expand on account of BPH, making testosterone substitution treatment a perilous choice for these men. Despite the risk, testosterone treatment has been shown to improve urinary symptoms in some men with BPH. This is guessed to be a consequence of metabolic improvement, compound or actual emasculation.
ANDROPAUSE TREATMENT CHOICES
While there is no remedy for advanced age; men with declining testosterone levels have a couple of choices accessible to assist with facilitating side effects related to “andropause.”
1. Lifestyle Considerations:
Before prescribing any treatments for men who are getting older, lifestyle considerations and the necessary adjustments should be made. Common sense maturing and illness are both vigorously impacted by unfortunate sustenance, carrying on with a stationary way of life, exorbitant liquor utilization and smoking. Testosterone creation is likewise known to be impacted by nourishment and digestion, as proven by hypogonadism in hefty men and men with metabolic syndrome. Men who devoured bunches of handled bread, cakes, dairy, pastries, and take-out dinners and who ate minimal dim green vegetables and home-cooked food sources would in general have low testosterone levels.
In this regard, expanding sustenance, keeping dynamic, and restricting both liquor utilization and smoking can work on the boundaries of maturing. As one ages, absorption will in general become dangerous, bringing about supplement malabsorption and age-related lack. Moreover, mature people will quite often eat less and feel less ravenous by and large, further decreasing dietary admission, actual limit and physical activity.
Expanding dietary admission of water-dissolvable fibre, dim green verdant vegetables, water, and food varieties rich in stomach-related compounds (like products of the soil) can assist with expanding supplement assimilation. Supplements with multiple vitamins and minerals may also be recommended. Notwithstanding, without a trace of illness, studies propose that the impacts of supplementation are insignificant contrasted with devouring a solid assortment of entire food varieties (natural products, vegetables, nuts, seeds, grains, and so forth).
2. Androgen Replacement Therapy:
: In the absence of disease, androgen supplementation is typically only prescribed for short periods to deficient individuals due to full-blown hypogonadism.
In this regard, chemical substitution treatment is turning into an undeniably famous choice for maturing men. A few men get benefits from enhancing androgens, including an expanded drive, less weakness and improved mood. Creature concentrates on uncovering that testosterone treatment might assist with further developing decreased bone thickness related to andropause.
Be that as it may, the review goes against results about testosterone swap treatment for mature men. The most important advantage gives off an impression of being gotten when care is taken to guarantee that chemical levels stay inside sound boundaries. DHT and estradiol, two testosterone-derived hormones that have the potential to exacerbate the onset of BPH, may be produced more frequently as testosterone levels rise.
Side Effects:
Adverse effects associated with androgen replacement therapy include increased red blood cell production and decreased HDL cholesterol production. In transdermal applications, testosterone therapy induced flushing, acne, and oily skin.
Contraindications:
Testosterone supplements are contraindicated for men with prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia and lower urinary symptoms or LUTS. Those with obstructive sleep apnoea, kidney disease and cardiovascular disease should also avoid testosterone supplementation.
3. Medication:
In men with prostatic enlargement as a result of aging, medications that manage symptoms are generally the first line of treatment. The doctor might prescribe the following types of drug: Alpha Blockers which block conduction of nerves to the prostate and help to lower prostatic contractions that result in urinary blockages.5-Alpha-Reductase Inhibitors that prevent the conversion of testosterone into DHT. This may help to lower the size of the gland and slow its growth.PDE-5 Inhibitors can help lessen erectile dysfunction, which is a common side effect of using alpha blockers and/or of testosterone deficiency.
Side Effects: Alpha blockers can cause dizziness, headaches, increased heart rate and weakness, especially when taken on the first dose.5-alpha-reductase inhibitors may contribute towards hair loss, hypogonadism, depression, decreased fertility and erectile dysfunction. PDE5 inhibitors might induce headaches, gastric reflux, flushing, muscle stiffness, back pain, low blood pressure, weakness, and dizziness. Severe side effects include irreversible vision and hearing loss.
Contraindications: Alpha blockers are contraindicated in the case of kidney impairment, history of cataract surgery, cerebrovascular disease, coronary artery disease and active respiratory infection.5-alpha-reductase inhibitors are contraindicated for men with hypogonadism who do not have prostatic enlargement. PDE5 inhibitors should not be taken by those who are at an increased risk for acquiring prostate and skin cancer as it may exacerbate disease onset.Any medication is contraindicated in the case of being allergic to any of the ingredients.
4. Prostate Surgery:
Surgical options for prostatic enlargement are only employed when symptoms get out of hand and threaten to cause bladder obstruction. Your doctor will only prescribe surgery when medication is non-responsive or symptoms require drastic action to be taken. The most common surgical procedure pertaining to the aging prostate would be a transurethral prostatic resection. The surgeon inserts a surgical tool through the urethra known as a resectoscope (similar to a larascope). This tool allows for the physician to see the enlargement and to cut away overgrown prostatic tissue that is causing a urinary blockage.As this does not address the underlying cause of the issue, transurethral resections may need to be repeated after some time when the prostate grows back. Some men opt for a prostatectomy in which the whole gland is removed. A doctor may suggest prostate removal if the gland is 100g or more (a normal size is roughly 22g on average).
Side Effects: Both types of surgery (especially full prostate removal) may cause “dry ejaculation” in which the ejaculate moves the wrong way and does not exit at the time of orgasm. This can result in male infertility, yet does not usually interfere with any other aspect of reproduction. Urinary tract infections are common complications after prostate surgery, as is painful urination for a few days’ post-surgery. Rare complications of transurethral resection include: Erectile dysfunction, Loss of bladder control Heavy bleeding.
Contraindications: Blood thinning medications and over-the-counter painkillers ought to be avoided a few days before surgery as they count as contraindications.Those with high blood pressure or kidney disease should not opt for prostate surgery due to the risk (even while low) of transurethral resection syndrome.
5. Botox Injections:
Botox is a risky (unofficial) treatment option that has been shown to be effective in some but not all cases of BPH, LUTS or overactive bladder. It’s mainly used as an alternative to medical treatment for unresponsive cases where severe urinary symptoms are concerned and where the patient is not a good candidate for surgery.The theory behind it is that Botox injected into the prostate can relax the muscles in the gland by blocking nerve conduction to it. Botox contains botulin toxin A which is a highly toxic substance that paralyzes nerves when injected into them. The body takes a long time to remove Botox, sealing it off at the injection site from the rest of the body and degrading it over the course of 2 years or longer. In some with chronic diseases that affect immune function, Botox has been shown to create a systemic infection, adding to the treatment risk.Previous studies have shown that it has the same efficacy as a placebo treatment, depending on the site of injection, who administers the treatment and the unique disposition of the patient.
Side effects:No side effects have been observed for prostatic Botox injections, as of yet. A lot more research and long-term follow up studies need to be conducted before one can rule out the possibility for potential adverse reactions to Botox.
Contraindications: Botox is contraindicated for those with active urinary tract infections, recurring urinary tract infections or who are allergic to botulin toxin. It is also contraindicated for those with motor neuropathies such as Parkinson’s disease or when using prescription muscle relaxants.
Conclusion
There is still debate as to whether andropause is a real condition or not. However, it is clear that blood testosterone levels tend to decline slowly in aging men, while tending to show an increase in the prostate. These age-related changes can be improved through healthy dietary and lifestyle choices and may also see improvements with testosterone treatment, in spite of inconclusive evidence.
In the event of disease such as prostatic enlargement, prescription drugs are advised. Surgery, botox and high-intensity ultrasound are other options for those with prostatic enlargement who do not respond to medications.
It is important to discuss any age-related treatment or therapy first with a healthcare professional, especially if disease is suspected, already present or if one is taking other medications that may cross-react.
admin
Related Posts

Spectrum Of Digital Marketing – Geeta University
Spectrum Of Digital Marketing – Geeta University Digital marketing has become a crucial aspect of modern-day marketing. With the rise of the internet, businesses have recognized the potential of online marketing, and the spectrum of digital marketing has been continuously

Virtual & Augmented Reality – Geeta University
Virtual & Augmented Reality – Geeta University Virtual and augmented reality have been gaining immense popularity in recent years, and it’s not hard to see why. These technologies offer immersive experiences that can transport users to different worlds and enhance
Mostbet Nadir Casino Mosbet Kazin Ugostiteljska Oprema Za Hotele I Restorane
Mostbet Nadir Casino Mosbet Kazin Ugostiteljska Oprema Za Hotele I Restorane2013-cü ildə yaradılıb və o vaxtdan ölkənin aparıcı bukmeker kontorlarından birinə çevrilib. Təbiidir ki, biz onlardan sadəcə vahid neçəsini burada qeyd etdik, mərc kontorunda yuxarıda gördüklərinizdən daha əhəmiyyətli, daha kreativ

